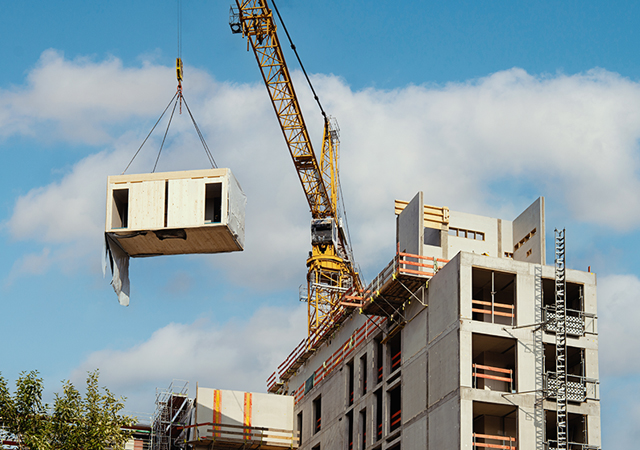
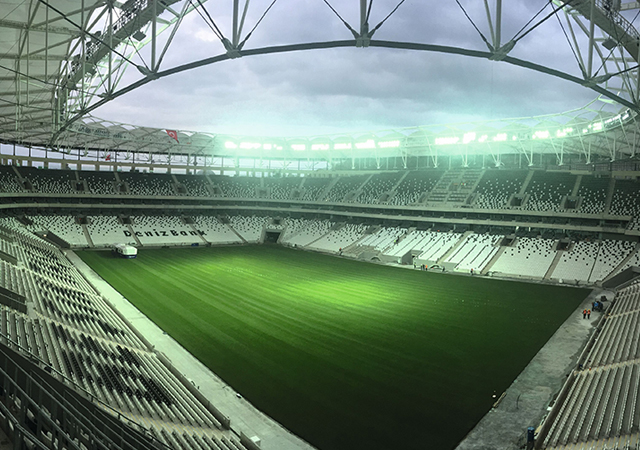
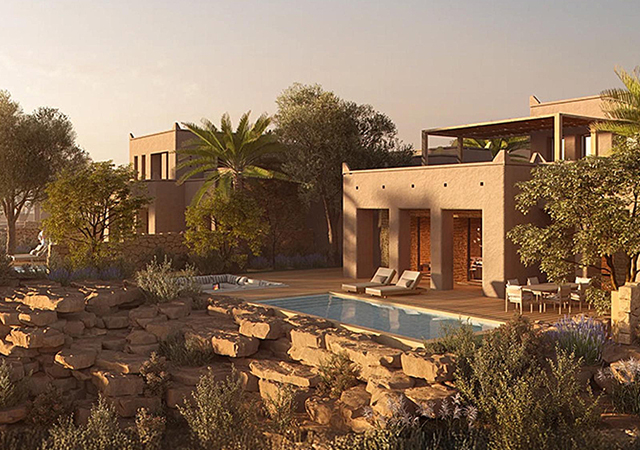
Volumetric modules are fully completed three-dimensional units, including rooms or building sections.
Volumetric modules are fully completed three-dimensional units, including rooms or building sections.
The construction landscape is evolving, and modular construction has emerged as a game-changing solution for the Middle East’s unique challenges. Unlike traditional building methods, modular construction involves assembling prefabricated units, or modules, in a factory setting, which are then transported to the site for installation. For a region experiencing rapid urbanisation and large-scale infrastructure projects, modular construction offers a viable pathway to meet growing demands efficiently and safely.
Different forms of modular construction
The primary forms of modular construction include:
• Volumetric modules are fully completed three-dimensional units, including rooms or building sections, fabricated in a controlled environment and ready for quick on-site assembly;
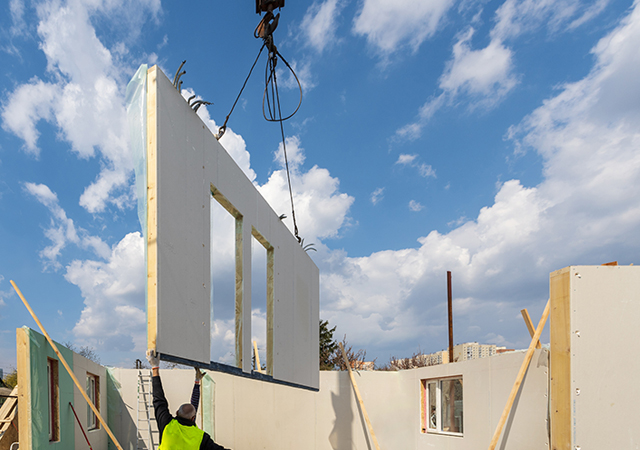
• Panellised construction relies on prefabricated flat panels for walls, floors and roofs, which are then assembled at the construction site, enabling adaptable layouts; and
• Hybrid solutions combine conventional building methods with prefabricated components, optimising both speed and design quality.
 |
|
Amer ... adoption of international building code ensures that modular buildings meet strict safety, structural and fire-resistance requirements. |
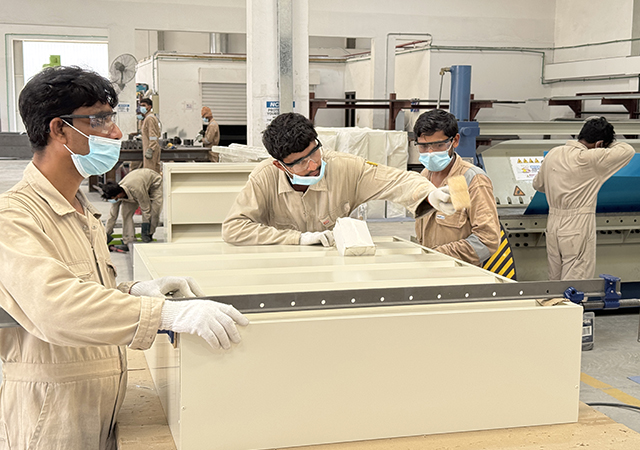
Once considered synonymous with trailers, mobile homes and temporary structures, modular construction has undergone a major transformation, thanks to technological innovations and materials. Today, it allows architects and builders to design and assemble complex, high-quality buildings quickly and efficiently, far surpassing the limitations of traditional on-site construction methods.
The materials used today are also key to the system’s versatility. Wood, steel and concrete are the primary resources employed, each bringing distinct benefits in terms of durability, cost-efficiency and environmental impact.
Challenges facing the industry
Despite its clear benefits, modular construction faces several obstacles that hinder its broader adoption. Transporting large, prefabricated units can be costly and carry a risk of damage.
Module dimensions are also limited by transportation regulations, which can constrain certain architectural projects. Additionally, modular construction also demands complex front-loaded planning, often involving advanced tools such as Building Information Modelling (BIM), which can be intimidating for firms unfamiliar with these processes.
 |
|
Colker |
Overcoming these hurdles will take time, but as more successful projects emerge, industry confidence is likely to grow.
Advantages of modular building in urban areas
GCC countries, including the UAE, Saudi Arabia and Qatar, are increasingly turning to modular construction to address challenges such as labour shortages, tight construction schedules and the need for high-quality, resilient buildings. Moreover, the adoption of international building codes and standards, including those created by the International Code Council (ICC), ensures that modular buildings meet strict safety, structural and fire-resistance requirements.
Modular construction offers clear advantages in dense urban environments. By fabricating structures off-site and assembling them quickly on-site, project timelines can be significantly reduced, often resulting in notable cost savings. This efficiency helps offset higher expenses tied to strict permitting and site requirements while also reducing the disruption caused by long construction activity.
 |
|
Panellised construction relies on prefabricated flat panels. |
Beyond time and cost savings, modular construction brings long-term environmental benefits to cities. Off-site fabrication generates far less waste than traditional on-site methods as manufacturing principles are incorporated, and waste materials are repurposed for other projects without the need for costly transport and storage. The use of energy-efficient and environmentally friendly materials further reduces impact, supporting broader sustainability goals.
For urban areas where land is scarce and community impact is a key consideration, modular construction provides a practical, sustainable path to meeting development needs.
Driving faster, safer and more sustainable growth
The speed of modular construction is one of its greatest strengths. By fabricating components in a controlled factory environment while simultaneously preparing the site, overall construction timelines can be drastically shortened.
This approach is especially valuable in the Middle East, where rapid development is crucial to support population growth and economic diversification.
Safety is another key benefit. Moving most of the work off-site reduces exposure to common jobsite hazards, lowering the risk of accidents, project delays and unexpected costs.
Standardised modular components ensure consistent quality, reducing risks associated with structural failures or non-compliance with building codes, further supported by international guidelines from organisations like ICC.
From a sustainability perspective, modular construction uses material more efficiently, produces less waste and supports energy-efficient building designs. Modules can even be designed for disassembly and reuse, promoting circular economic practices that align with the region’s growing climate-conscious policies.
Finally, modular construction helps meet the rising demand for efficient solutions in sectors such as urban infrastructure, healthcare and housing. With urban populations expanding, conventional construction methods often struggle to keep pace with timelines and quality expectations.
The Future of Off-Site in the Middle East
The Middle East is at a pivotal stage in its development, where construction choices will shape the region’s urban landscape for years to come.
By adopting off-site modular techniques and adhering to international standards, countries in the GCC and across the Middle East can accelerate growth, improve safety and advance sustainability, positioning themselves as leaders in innovative and responsible construction practices.