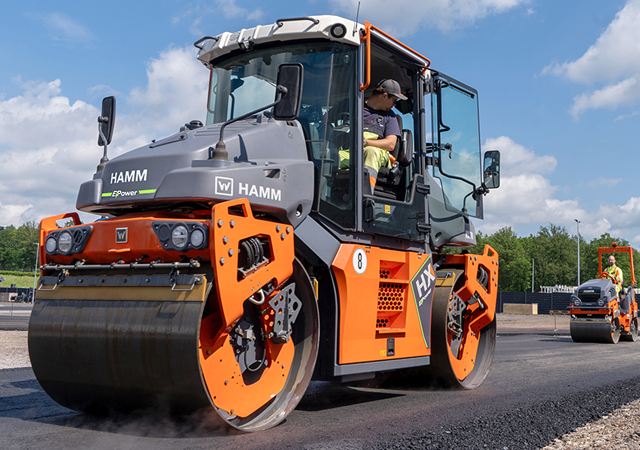
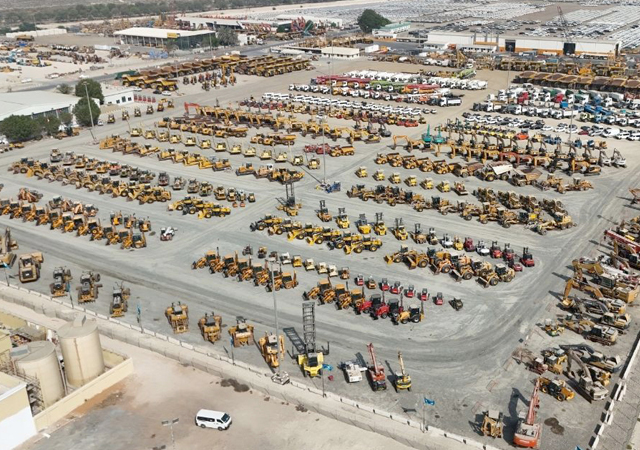
Hamm’s HX 70e VV-S, a fully electric roller ... designed to eliminate operating emissions.
Hamm’s HX 70e VV-S, a fully electric roller ... designed to eliminate operating emissions.
Hamm, a compaction specialist which is part of the Germany-based Wirtgen Group, recently introduced its latest battery-powered tandem rollers, stepping up efforts to eliminate operating emissions from road construction machinery.
The new pivot-steered HX 70e VV-S, a fully electric roller with two vibration drums, is designed for use on inner-city construction sites, where reducing noise and exhaust emissions is becoming a regulatory requirement. A second variant, the HX 70e VO-S, uses an oscillation drum and will also be introduced as a sales variant.
Powered by a 400-volt, 63 kWh lithium-ion battery developed with Austria’s Kreisel, the HX 70e can be charged via a Type 2 connector, with additional compatibility for Type 1, J1772, and CCS charging systems planned. With fast charging, the battery can be replenished from 20 per cent to 80 per cent in under an hour.
“Owing to the electrical components, the battery-powered electric tandem rollers are not only quieter but also more efficient in operation than their diesel-driven counterparts. This is especially true of the models with the oscillation drum,” says a spokesman for Hamm. “Here, the already low noise of oscillation is combined with the quiet electric drive, making the machines the perfect choice for use in vibration-sensitive and noise-sensitive environments, such as in the vicinity of hospitals or historical buildings.”
 |
|
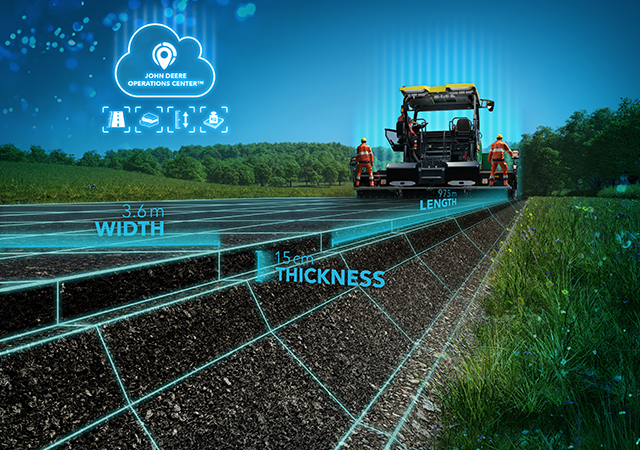
Wirtgen Group Performance Tracker uses basic paving data to calculate the amount of material already laid. |
The new HX 70e tandem rollers deliver the same compaction power as the diesel-engined machines and in fact produce a higher output at their peak, he says. The battery-powered electric rollers are operated in virtually the exact same way as the conventional diesel counterparts, with the only difference being the display, which now features new symbols to give operators an intuitive user experience.
The company highlighted lower operating costs due to reduced maintenance needs compared with diesel engines. The rollers can also be integrated with the John Deere Operations Center, allowing users to track operating data and plan maintenance schedules.
Meanwhile, another Wirten Group company, Joseph Vögele, a leading road paver manufacturer, has introduced a range of new automatic functions and digital solutions designed to improve precision, efficiency, and safety in asphalt paving. These include the automatic steering and width control system AutoTrac, the fully automated Smart Pave digital control system, the Wirtgen Group Performance Tracker Paving for comprehensive construction site documentation, and the RoadScan temperature measurement system. All of these technologies have been specifically developed and integrated as part of Vögele’s latest Dash 5 paver generation.
 |
|
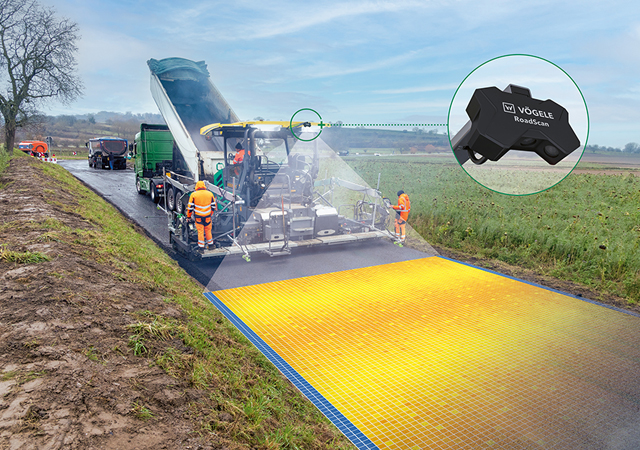
RoadScan temperature measurement system features a sensor width increased by 3 m to 13 m and improved resolution. |
AutoTrac uses sensors and physical references such as kerbs and stringlines to control the paver’s width and direction. This system reduces operator workload and material waste by enabling precise edge detection and automated screed width adjustment.
Smart Pave operates using virtual references stored in the John Deere Operations Center digital platform. It integrates high-precision positioning through a dual-antenna GNSS system permanently mounted on the machine, allowing automatic control of pave width, position, and direction without manual assembly or extensive data handling by operators.
The Wirtgen Group Performance Tracker Paving system uses basic paving data such as section length, layer width, layer thickness and material density to calculate the amount of material already laid. Material deliveries can be recorded quickly and easily and additional relevant data such as CO₂ emissions and fuel consumption can be mapped. This data can be accessed and analysed via the John Deere Operations Center, enabling integrated management of milling, paving, and compacting processes.
The latest RoadScan temperature measurement system was also presented, featuring a sensor width increased by 3 m to 13 m and improved resolution. It leverages the existing GNSS antenna system, reducing sensor size and weight for easier mounting.