What are the top three trends currently shaping Kuwait’s construction sector? What factors will significantly influence its growth in 2025-26?
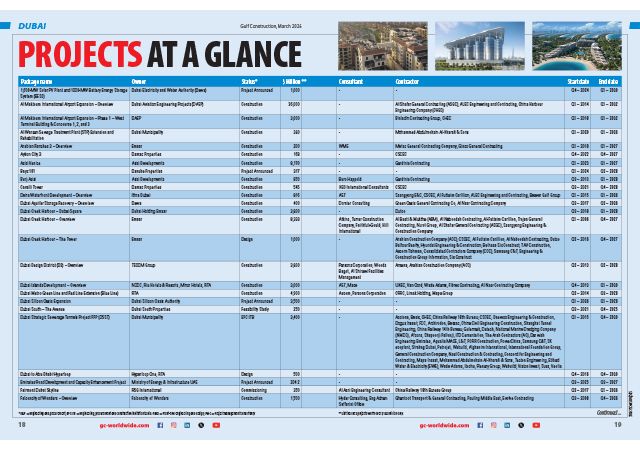
Kuwait’s construction sector is currently being shaped by three major trends that are expected to significantly influence its trajectory in 2025-26. Firstly, there has been a noticeable reduction in government spending on large-scale infrastructure and mega projects, with many major expenditures being deferred to future budget years.
Secondly, there is an increasing emphasis on public-private partnership (PPP) projects, where the government is actively issuing investment opportunities for private developers and EPC (engineering, procurement, and construction) contractors to collaborate on. This approach has already seen success through initiatives led by the Public Authority for Housing Welfare (PAHW).
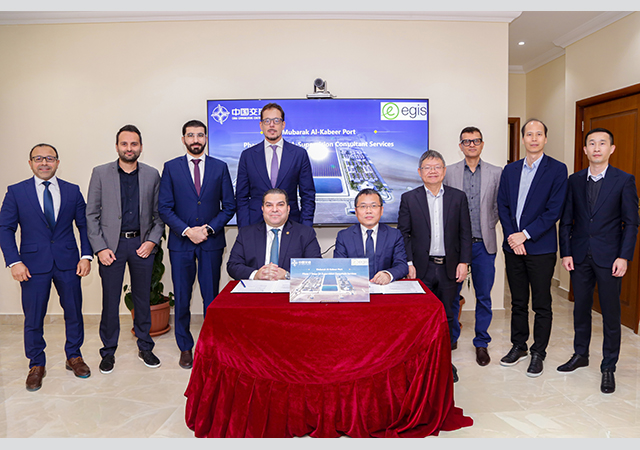
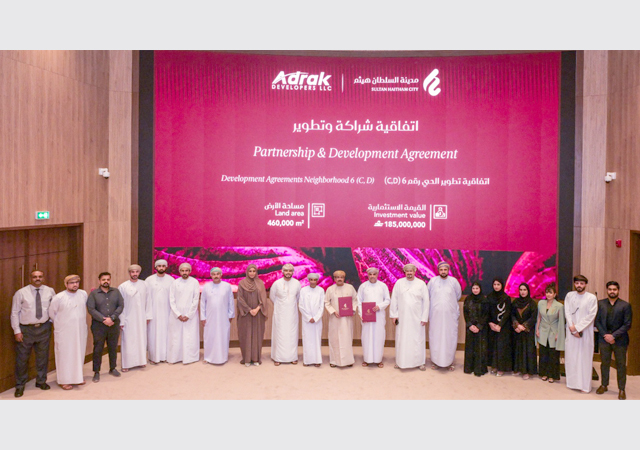
Lastly, Kuwait is activating its trade and collaboration memorandum of understanding (MOU) with China, paving the way for large projects to be funded, executed, and operated by Chinese development banks and corporations. A key example of this is the recently signed Mubarak Port agreement, with similar discussions under way for other projects.
 |
|
Shuaib ... committed to delivering impactful projects. |
What are the most effective policy changes or regulatory adjustments that could stimulate growth in Kuwait’s real estate and construction sectors?
One of the most critical reforms involves updating and amending the Public Tender Laws, particularly for technically complex and sensitive projects. Under the current framework, contracts are often awarded to the lowest bidder, which may not always ensure the best quality or long-term sustainability of the project. Implementing a weighted evaluation system that considers both technical and financial factors would allow awards to be granted to the most competent contractors, rather than simply the cheapest.
Another essential step is the finalisation and publication of Kuwait’s Fourth Master Plan. The current masterplan is outdated and no longer aligns with the country’s evolving societal, economic and infrastructural needs. A revised and forward-looking masterplan would unlock new development and investment opportunities that accommodate modern demands.
Additionally, revising and consolidating Kuwait’s fragmented PPP laws into a single, comprehensive framework is crucial for facilitating large-scale investments. At present, the Kuwait Authority for Partnership Projects (KAPP) law is on hold, the Build-Operate-Transfer (BoT) law remains inactive, and the Public Auction Decree 1/2023 is unsuitable for major investment projects. A unified PPP law that incorporates the successful exemptions granted to the PAHW would create a more streamlined and effective legal environment. This would enable various government entities to efficiently collaborate with private sector partners, ultimately accelerating project execution and enhancing economic growth across multiple sectors.
Furthermore, mandating Building Information Modelling (BIM) adoption in Kuwait’s construction sector would drive efficiency, sustainability, and growth. Countries with BIM mandates benefit from structured digital workflows, enhanced collaboration and ISO 19650 compliance. Enforcing BIM as a contractual requirement would improve project quality, co-ordination, and cost-effectiveness by reducing errors, delays, and material waste. Additionally, streamlined processes would boost investor confidence, accelerate approvals and attract global developers. By setting clear BIM regulations, Kuwait can establish itself as a leader in digitally-enabled, resilient and sustainable construction.
Which specific projects or initiatives within the New Kuwait 2035 plan are demonstrating the most significant progress in the construction sector? What are the key challenges hindering further advancement?
Among the New Kuwait 2035’s promising initiatives is the Abdalli Economic Zone, which is strategically positioned to drive economic growth and regional trade. The project is ready for immediate execution, but its progress is contingent on securing the necessary funding.
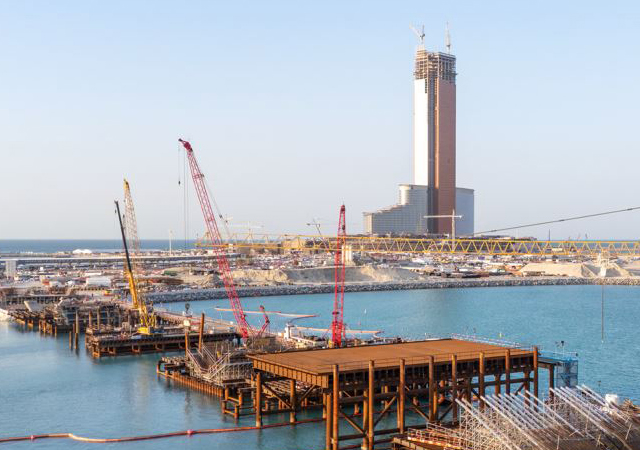
Another critical project is the Mubarak Al-Kabeer Port, which holds significant potential for boosting Kuwait’s maritime trade capacity. Recently, an agreement has been signed between the Ministry of Public Works (MPW) and a Chinese government company to take the project forward.
Additionally, major infrastructure upgrades such as the Fourth Ring Road and Road 30 enhancement projects have the potential to move forward if good planning and management are applied. Previous road infrastructure projects, like the successful Jahra and Jamal Abdel-Nasser road developments, have demonstrated that with effective project oversight, similar transportation projects can be reactivated and completed efficiently.
 |
|
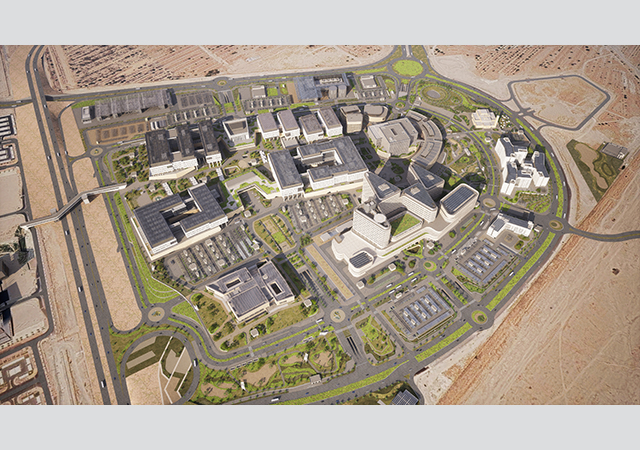
Kuwait University Health Science Centre (KUHSC) ... Pace implemented a Common Data Environment to manage the complexity of this large-scale academic facility. |
What are the three most significant shifts in the construction industry that Pace is preparing for in the next five years? How is Pace strategically positioning itself to capitalise on these changes?
The most notable industry transformation is the expansion of the Saudi Arabian construction market. Pace is at the forefront of the kingdom’s Vision 2030, committed to delivering impactful projects for the nation.
Another key shift in the industry is Kuwait’s increasing reliance on PPP and private sector funding for government projects. Pace has already played, and will continue to play, a pioneering role in successful PPP initiatives and is well-positioned to collaborate with EPC firms, project owners and government authorities across various capacities.
The firm is also embracing technological advancements in digital design and construction methodologies. The full-scale integration of BIM across all project phases is becoming a standard requirement internationally. While BIM adoption in Kuwait is still consultant-driven, Pace has proactively implemented BIM workflows in multiple markets where strict mandates exist. By ensuring full-lifecycle BIM implementation – from concept design to construction and asset management – Pace enhances project efficiency, accuracy and coordination.
Sustainability and smart building technologies are also central to modern construction, with a growing focus on low-carbon, resource-efficient, and intelligent infrastructure. Pace is embedding sustainability principles from the early design stages, optimising material use, and assessing environmental impacts to align projects with green building certifications and climate-conscious goals.
Smart buildings, 5D BIM and advanced modular construction are interconnected in their ability to enhance efficiency, performance and sustainability, but their success depends on early-stage integration across all project stakeholders. Smart buildings optimise operational expenditure (OPEX) efficiency through sensor-driven automation of environmental controls, security, maintenance, and energy management. Advanced modular construction extends beyond prefabricated components to a holistic construction methodology, incorporating MEP systems and factory-based assembly for higher quality, faster execution, and reduced on-site risks. Bridging smart buildings and modular construction, 5D BIM integrates spatial, quality and performance data with time and cost analysis, enabling better decision-making, reduced risk and optimised project delivery.
Additionally, automation and digital transformation are reshaping project delivery by enabling automated workflows, real-time data analytics, and improved compliance checks. Pace is investing in advanced model coordination and data-driven decision-making, allowing for more efficient execution and reduced project risks. A major innovation in this domain is the adoption of digital twins, which revolutionises post-construction asset management by facilitating real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance and lifecycle tracking. Pace ensures its project data and information management structures support seamless digital twin integration, enhancing facility management capabilities for clients.
To stay ahead of these industry shifts, Pace is actively upskilling its workforce in digital construction methodologies, sustainability, and data-driven insights. The firm is also attracting specialised talent and standardising internal workflows to expand BIM adoption, sustainability strategies and digital project management. As part of its commitment to industry advancement, the company is advocating for stronger BIM adoption in Kuwait, supporting stakeholders in transitioning towards more structured digital workflows.
 |
|
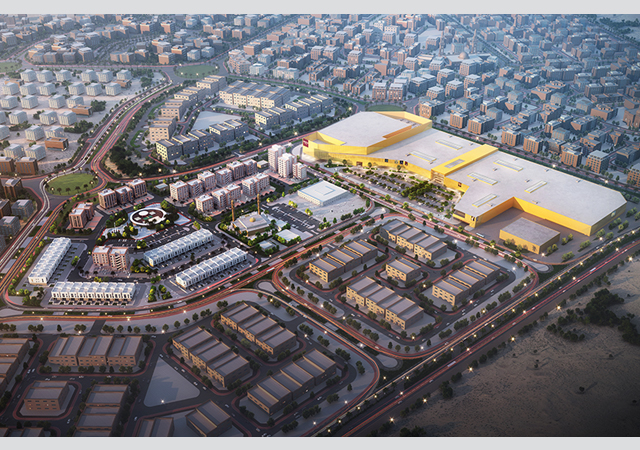
Aventura (J3) project taking shape in Jaber Al-Ahmad City. |
Highlight two or three key projects that showcase Pace's expertise and address significant challenges. What unique design elements or technological approaches are being employed, and what is the current project status?
The Assima Mixed-Use Development in Kuwait City is a landmark 54-storey tower that required an innovative structural solution to optimise material usage. The design team implemented voided concrete technology, significantly reducing the overall concrete volume and lowering the tower’s weight without compromising structural strength. This innovative approach not only enhanced the project’s sustainability by minimising material consumption but also earned Pace an American Concrete Institute (ACI) award for its engineering excellence.
Pace has been instrumental in the development of the Kuwait University Health Science Centre (KUHSC), a large-scale academic facility that required coordination across 520 federated models involving 23 international consultants. To manage this complexity, Pace implemented a Common Data Environment (CDE), facilitating real-time information exchange to enhance efficiency and transparency among stakeholders. Advanced 3D spatial coordination and automated clash detection were utilised to prevent design conflicts, ensuring a seamless integration of various design components. The project is nearing completion, reinforcing Pace’s ability to manage high-profile institutional developments with cutting-edge BIM-driven issue management.
Pace is also contributing to a Research & Innovation Campus on the west coast of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, a cutting-edge project that involves complex multi-disciplinary integration across multiple stakeholders. To address coordination challenges, Pace has employed automated model health checks and digital reviews for quality assurance. The project leverages Power BI dashboards for real-time project insights and reporting, enabling seamless decision-making and efficient project tracking. This advanced digital workflow ensures that the project remains on schedule and maintains the highest quality standards.
What are the potential impacts of AI on the construction industry’s labour market in the region? How is Pace preparing its workforce for these changes?
AI is set to bring significant changes to the construction industry’s labour market in the region by automating repetitive tasks, streamlining workflows, and improving decision-making. As AI-driven design tools become standard, there will be a reduced reliance on manual drafting and documentation, allowing professionals to focus more on strategic and creative aspects of their work.
Additionally, AI-powered workflow automation is expected to handle many administrative project management tasks, such as tracking Requests for Information (RFIs), scheduling, and ensuring compliance. The rise of AI agents and agentic processes will further optimise construction workflows by managing admin-heavy responsibilities like automated clash detection, compliance checking, and real-time data analytics.
To prepare for these changes, Pace is proactively investing in AI training and upskilling programmes for its employees. By equipping its workforce with the knowledge and expertise to work alongside AI tools, the company ensures that automation enhances productivity rather than replaces human oversight. In addition, Pace is implementing automated project workflows to improve efficiency while maintaining human-led decision-making, ensuring that AI supports but does not override professional expertise. Recognising the growing role of AI-driven processes in construction, Pace is also focusing on training its digital delivery and BIM managers and coordinators to oversee AI-assisted workflows effectively. This approach guarantees that AI integration remains structured, responsible and aligned with the company’s commitment to innovation and quality.
 |
|
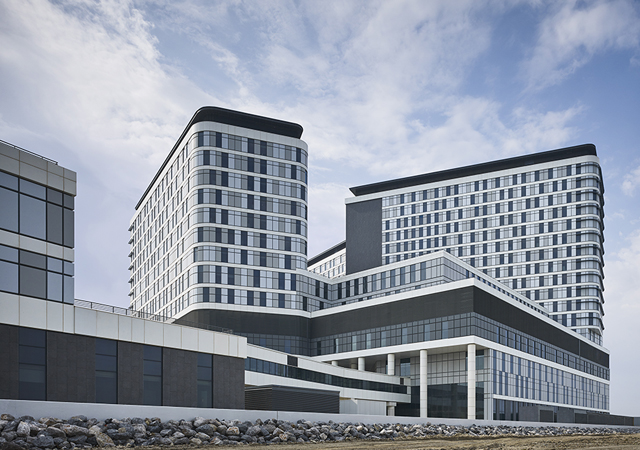
The Pace-designed New Maternity Hospital ... completed last October. |
Provide examples of how Pace is implementing AI in design, construction, or project management to enhance efficiency and innovation.
Pace is actively integrating AI into various aspects of design, construction, and project management to enhance efficiency, innovation, and decision-making.
While AI adoption is still evolving, the firm is experimenting with generative AI tools and data-driven insights to improve workflows, optimise project delivery and support creative processes – without replacing the human-driven design expertise that defines Pace’s unique approach.
Pace is leveraging generative AI tools such as AutoDesk Frame, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion to accelerate the early design phase. These AI-driven platforms enable rapid text-to-image generation, helping designers quickly visualise concepts and iterate on creative ideas.
AI is also playing a growing role in data analysis and business intelligence at Pace. The company utilises Power BI and CoPilot tools to extract insights from business performance metrics, helping its leadership make informed, data-driven decisions. Additionally, Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-powered AI assistants, support daily workflows by automating repetitive tasks like generating meeting minutes, reports and project documentation, as well as providing AI-powered chatbots for quick access to project standards and best practices.
To enhance design accuracy and efficiency, Pace is leveraging AI-driven model health checks and quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC) tools. These technologies help perform automated compliance checks and clash detection, identifying potential design conflicts before they escalate into costly construction errors.
In project management, Pace is evaluating AI-powered tools for automated reporting, real-time tracking and workflow optimisation. AI solutions are being explored for predictive scheduling, risk management and resource optimisation.
While AI enhances operational efficiency, Pace maintains strict governance and oversight over its use, particularly concerning Intellectual Property (IP) protection. Given that AI tools often require training on existing data, Pace ensures that AI adoption adheres to ethical and legal standards, preventing any infringement of proprietary or confidential project data.
 |
|
The 54-storey Assima Mixed-Use Development utilised voided concrete technology. |
What are the newest or most innovative services and specialisations Pace has introduced? How are these services addressing evolving market needs?
Pace has recently integrated the Program Management Office (PMO) and Digital Delivery services across all its offerings. This strategic shift enables Pace to manage highly complex projects involving multiple stakeholders with greater efficiency, ensuring streamlined coordination and optimal project outcomes.
A key area of innovation is Pace’s BIM Management Services, which address the growing need for structured project execution and enhanced collaboration. The newly expanded Digital Delivery department provides comprehensive BIM and Information Management services, fully aligned with ISO 19650 standards.
Pace’s structured Digital Delivery approach facilitates seamless coordination among all stakeholders, significantly reducing errors and rework. The adoption of CDEs allows for real-time information exchange, improving project efficiency, transparency, and decision-making processes. This ensures that all project participants – clients, contractors, consultants, and government entities – have access to up-to-date, reliable data, enhancing overall project management and execution.
Beyond digital transformation, Pace has also introduced sustainability-driven assessment methodologies that evaluate embodied carbon impact and material efficiency in its projects. These methodologies help clients make informed decisions regarding material selection, energy use and overall environmental impact, reinforcing Pace’s commitment to sustainable and responsible design. By integrating these green building principles into its services, Pace is ensuring that its projects align with global sustainability targets while delivering cost-effective and environmentally conscious solutions.
How is Pace adapting its organisational structure or talent development strategies to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market?
A key initiative in this transformation is the implementation of the latest Human Experience Management (HXM) platforms, which enhance talent acquisition, retention and professional development. By leveraging these advanced systems, Pace ensures that it can attract, nurture, and retain top-tier expertise, fostering a workforce that remains competitive and well-equipped for future industry challenges.
In response to the significant expansion in the Saudi market, Pace has also been expanding and restructuring its Centre of Excellence (CoE) to strengthen its presence in Saudi Arabia. This initiative ensures that Pace can provide localised expertise and specialised resources to support the increasing demand for large-scale infrastructure and construction projects in the region.
Additionally, Pace has introduced a comprehensive Knowledge Management and Learning & Development (L&D) strategy designed to keep its workforce digitally fluent and future-ready. This strategy includes competency-based learning paths tailored to different roles, ensuring that employees receive structured and targeted professional development. The firm has also established the Pace Digital Knowledge Platform (DKP), which integrates a Learning Management System (LMS), internal training modules and structured skill assessments. This system allows for effective skill tracking and continuous professional growth.
To further enhance engagement and efficiency, Pace has adopted micro-learning and blended training formats, offering employees flexible and interactive learning experiences. These innovative training approaches help professionals stay updated on the latest industry trends and technologies without disrupting their workflow. Additionally, knowledge-sharing initiatives within the organisation foster collaboration and best practices, ensuring that Pace remains at the forefront of technological innovation and industry leadership.
Describe Pace's key sustainability and digitalisation initiatives, including the implementation of technologies like BIM and digital twins.
Pace is at the forefront of the industry’s sustainability and digitalisation initiatives. The company is actively incorporating carbon assessment and material efficiency into its design processes to align early-stage decisions with sustainability goals. By evaluating the carbon footprint and lifecycle impact of materials, the firm ensures optimised material usage and reduced environmental impact.
A key focus area for sustainability is the development of energy-efficient and smart buildings. Through embedding structured BIM workflows and asset information management into projects, Pace provides clients with the necessary data to implement smart building technologies that enhance energy efficiency, predictive maintenance and long-term operational planning. These capabilities enable real-time performance monitoring, helping optimise building operations for minimal energy consumption and maximum efficiency.
Additionally, Pace integrates lifecycle planning and sustainable construction practices into its BIM workflows to ensure resource efficiency throughout a project's lifespan. By embedding sustainability considerations into design coordination, procurement and construction processes, Pace ensures that environmental responsibility is not just a final-stage consideration but an integral part of the project lifecycle.
Meanwhile, Pace is fully committed to digital transformation, with BIM serving as the foundation for structured project execution. The firm applies ISO 19650-compliant BIM processes from design to construction and asset management, ensuring data consistency, efficiency and accuracy. In implementing CDEs, automated model health checks, and real-time clash detection, Pace minimises coordination errors before construction begins, significantly reducing rework and inefficiencies. Its BIM strategy also includes 3D modelling, immersive visualisation, model-based quantity take-offs and issue tracking, ensuring that data is well-organised throughout the entire project lifecycle.
To further enhance digital project execution, Pace is supporting digital twin integration, enabling long-term asset performance monitoring and predictive maintenance strategies. The firm ensures that BIM models, structured data workflows, and asset tagging are aligned with digital twin requirements, allowing clients to integrate these advanced systems when needed.
Pace also enhances data-driven project management by leveraging Power BI dashboards for automated reporting and real-time project insights. These dashboards consolidate design, construction, and financial data into structured, visual formats, enabling proactive decision-making, risk assessment and efficient resource allocation.
Which regional markets are key to Pace's growth strategy, and what are the specific plans for expansion in these areas?
Pace’s growth strategy is strongly focused on regional expansion, with particular emphasis on Saudi Arabia as the primary market. The booming construction sector in the kingdom presents sustainable and long-term opportunities for infrastructure, mixed-use developments and urban expansion. The resilience and stability of the Saudi market make it a key area for investment and strategic growth, and Pace is actively positioning itself to capitalise on this momentum.
Beyond Saudi Arabia, Oman and the UAE represent new markets for expansion, offering additional opportunities for international collaborations. These markets come with their own set of risks and challenges, requiring Pace to adapt its business strategies, operational frameworks, and market entry approaches.
Is there anything else you'd like to highlight regarding the future of Kuwait's construction sector or Pace's role within it?
The future efficiency and success of the construction sector is increasingly tied to the adoption of BIM and intelligent target planning tools. Pace is working with government entities, universities, and industry organisations to promote BIM education and awareness, ensuring that future professionals are well-equipped for digital construction methodologies.
Pace is also conducting training and workshops for government entities, highlighting the benefits of BIM mandates and their success in other markets. Additionally, the firm is supporting clients in defining clear contractual BIM requirements, reinforcing the need for client-led enforcement to drive structured BIM integration across projects.
While momentum is building for BIM adoption in Kuwait, regulatory support remains essential to ensure a fully BIM-integrated construction industry.