A renewable energy startup in the US backed by Bill Gates is developing an unconventional wind turbine system designed to help meet the rapidly growing power requirements of artificial intelligence and hyperscale data centres.
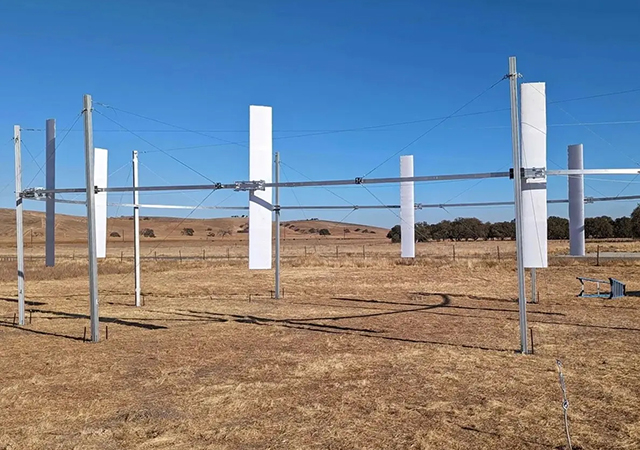
Airloom Energy’s design reimagines the traditional wind turbine architecture. Instead of vertical towers and large rotating blades, the system features a series of adjustable wings connected along a horizontal track. As the wings circulate, they capture wind energy and generate electricity. The low-profile structure stands far shorter than conventional horizontal-axis turbines and, according to the company, uses roughly 40 per cent less material and 96 per cent fewer unique components.
This streamlined configuration offers potential advantages in both cost and scalability. Airloom says the simplified structure could reduce manufacturing complexity and maintenance demands, making large-scale deployment more practical. The company claims its modular system could shorten project development timelines by up to 85 per cent, cutting the typical five-year lead time from planning to deployment for utility-scale wind farms to less than a year. Cost of energy generation could also be nearly halved compared with conventional wind installations, according to early estimates.
Another key factor is location flexibility. The compact turbines can operate in areas unsuitable for traditional wind projects, including zones near airports, coastal islands or mountainous regions where tall towers face technical or regulatory constraints. Because the system’s components are developed for mass production and easier transport, installation can be achieved with fewer logistical challenges – an advantage in both developed and emerging markets.
Airloom presented its engineering concepts and early pilot site results at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2026 (January 6 to 9), highlighting the technology’s potential to supply renewable power directly to energy-intensive industries such as AI computing, data hosting, and cloud infrastructure, helping operators scale sustainably while easing pressure on local grids.