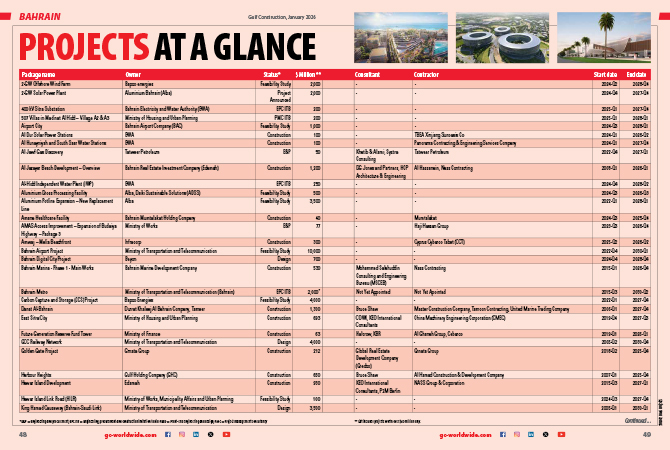
 Masa uses modern pest control techniques.
Masa uses modern pest control techniques.
MOHAMMAD ARIF HUSSAIN, an entomologist at Saudi-based Masa Establishment*, stresses on using a holistic approach to eliminate pests in building interiors
The interiors of buildings can provide shelter for various kinds of pests to hide and survive and the problem is exacerbated where proper hygiene and sanitation measures are not maintained.
A number of pest problems start in buildings where carpets are not properly cleaned, leading to rapid infestation by ants, beetles, and cockroaches, etc.
Floor coverings and carpets give an aesthetic look to the whole interior setting, protect the structure and help in maintaining the internal environment and sanitation. But if not installed properly, they may sometimes provide hiding places for insect pests.
Apart from ants and beetles, cockroaches too start hiding on the sides of carpets if not properly cleaned. Bedbugs may lay eggs and hide in the carpets, especially on the sides, and near the wall skirting and in the corners of the room; and their infestation becomes difficult to eliminate. Carpet beetles live and proliferate under the carpets, around skirting boards and in wardrobes and cause damage. The larvae of carpet beetles infest and eat the woolen and synthetic fibres of carpets, wool, fur, leather and silk.
Every dollar spent on insect pest prevention will return additional dollars in reduced product losses. Prevention is one critical factor in any effective pest management programme, and takes many forms, with two basic forms being exclusion and sanitation. Keeping pests outside, along with proper sanitation inside, helps prevent infestation and leads to a more organised, more efficient and safer workplace.
 |
Masa uses modern pest control techniques. |
As a pioneer in pest control and management in Saudi Arabia, Masa Establishment tackles pests through its integrated pest management (IPM) programme using a holistic approach. Shared responsibilities in environmental manipulation to control insects are the latest trends in IPM. Common interior pests are controlled by basic sanitation and good housekeeping strategies, with a reduction in the use of chemical controls.
Masa can provide an overall pest management programme with Care (consistency, accountability, responsiveness and effectiveness).
In nonchemical pest control methods, a number of guidelines need to be followed to reduce interior pest problems. These include:
• Trimming exterior plants and shrubs;
• Keeping windows and doors shut, or screened when open;
• Reducing storage areas where insects can nest in the interiors;
• Thoroughly vacuuming and dusting all areas. This helps determine whether the insect activity is current or old;
•Chemical applications can be used after these guidelines are followed.
Pests are not only a problem when they invade homes and cause structural damage, but they also carry a host of diseases. In fact, bacteria and viruses that cause gastroenteritis are often carried by pests such as cockroaches. From a health viewpoint, it is essential to locate pest hiding places and eliminate them within the home.
 |
Mousaied Al Shieshakly, owner and general manager of Masa. |
IPM approach
IPM is a process that can solve pest problems while minimising risks to people and the environment. It can be used to manage all kinds of pests anywhere – urban, agricultural, and wildland or natural areas.
IPM programmes use current, comprehensive information on the lifecycles of pests and their interaction with the environment. This information, in combination with available pest control methods, is used to manage pest damage by the most economical means, and with the least possible hazard to people, property, and the environment.
Urban IPM is a process for balancing the risks associated with pests and pesticides to achieve long-term pest suppression. It uses a wide variety of management practices. Control strategies in an IPM programme extend beyond the application of pesticides to include structural and procedural modifications that reduce the food, water, harbourage, and access used by pests.
In IPM, monitoring and correct pest identification help decide whether management is needed. Monitoring includes checking a field, landscape, forest, building, or any other site to identify the presence of pests, their numbers and damage caused. Correctly identifying the pest is key to knowing whether it is likely to become a problem and determining the best management strategy.
After monitoring and considering information about the pest, its biology, and environmental factors, it can be decided whether the pest can be tolerated or whether it is a problem that warrants control. If control is needed, this information also helps in selecting the most effective management methods and the best time to use them.
The most effective, long-term strategy to manage pests is by using a combination of methods that work better together than separately. Approaches for managing pests are often grouped in the following categories:
• Biological control: This is the use of natural enemies – predators, parasites, pathogens, and competitors – to control pests and their damage. Invertebrates, plant pathogens, nematodes, weeds, and vertebrates have many natural enemies;
• Cultural controls: These are practices that reduce pest establishment, reproduction, dispersal, and survival. For example, changing irrigation practices can reduce pest problems, since too much water can increase root disease and weeds;
• Mechanical and physical controls: These are used to kill a pest directly or make the environment unsuitable for it. Traps for rodents are examples of mechanical control. Physical controls include mulches for weed management, steam sterilisation of the soil for disease management, or barriers such as screens to keep birds or insects out;
• Chemical control: This entails the use of pesticides. In IPM, pesticides are used only when needed and in combination with other approaches for more effective, long-term control. They are selected and applied in a way that minimises their possible harm to people and the environment. Masa uses the most appropriate pesticide that will do the job and is the safest for other organisms and the environment.
* Masa Establishment is based in Jeddah and owned by Mousaied S Al Shieshakly, who is also the general manager. It is one of the biggest pest control companies in Saudi Arabia with 12 branches across the kingdom.








.jpg)



.jpg)



























.jpg)
































