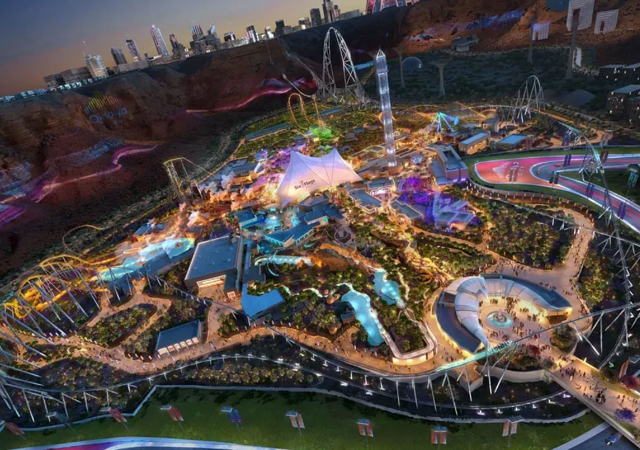
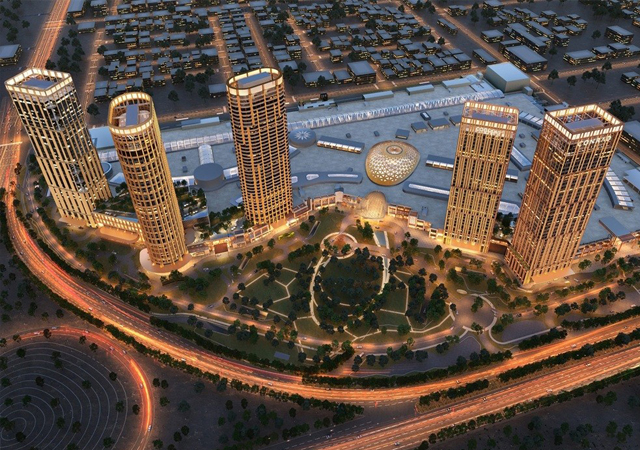
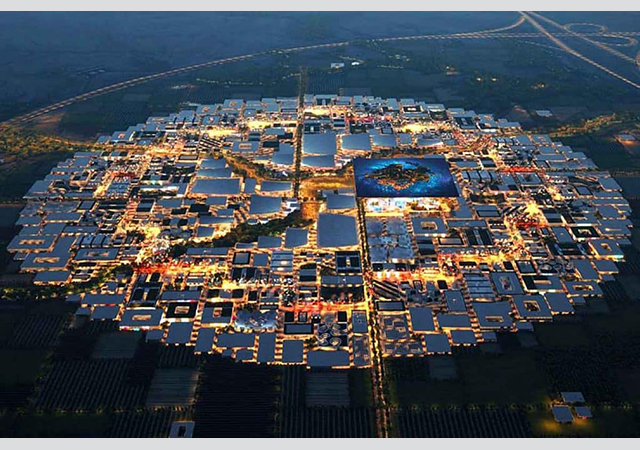
Concept of a futuristic hotel made possible using the metaverse.
Concept of a futuristic hotel made possible using the metaverse.
The metaverse concept has evolved as a transformative digital space with broad implications across numerous businesses in the dynamic environment of the digital era.
The potential of the metaverse to offer immersive experiences, digital twins, and virtual land ownership can completely reshape urban design and architecture. Its significance in shaping the urban landscape, particularly within the Arabian Gulf region, should not be underestimated, given the rapid expansion and remarkable technological advancements in the area.
URBAN PLANNING: A DIGITAL FRONTIER
Imagine a digital space where stakeholders gather to collaborate and design urban development blueprints – this is the metaverse’s influence on urban planning. Creating digital twins, in essence, virtual replicas of real cities is paving the way for a new era. Digital twins empower urban planners to monitor urban systems in real-time. The metaverse provides architects and urban planners with the freedom to design smart cities and eco-friendly infrastructure without being bound by geography.
 |
|
Huber ...digital twins are central to the metaverse’s urban planning potential. |
In the context of urban planning, citizens and people from all demographics would have more access to blueprints and development plans in the metaverse. With more access to virtual open houses, developers and architects would find it easier to broaden their market base internationally by utilising the metaverse.
Metaverses can be open environments, which would optimise market and environmental testing costs. Urban planners can use real-time data visualisation to see how a development project would look in any given geographical context.
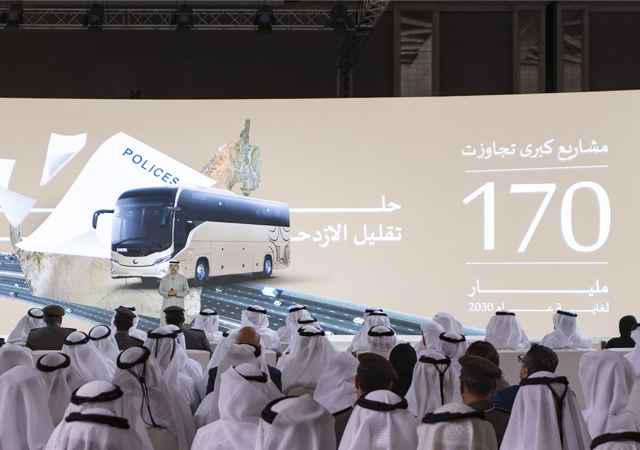
Right in the heart of the Arabian Gulf, the metaverse’s potential is shining through. Think about Damac’s recently established division D-Labs in the UAE, using virtual cityscapes to shape future urban landscapes. In Saudi Arabia, Neom’s digital twin created by Tonomus showcases how smart planning can be elevated through digital counterparts. Moreover, the UAE’s virtual city is weaving the metaverse into the very fabric of urban development.
DIGITAL TWIN TECHNOLOGY IN URBAN PLANNING
Digital twins are central to the metaverse’s urban planning potential. They let planners visualise different scenarios, such as switching up traffic patterns or building new structures, all in a virtual world. Through real-time data integration from sensors and IoT devices, these digital twins stay updated with real-time information and data. The significance to stakeholders for any development is that for any given project, there are many players to take into consideration.
• The funding: It is typical for development projects to have a high degree of leverage. With loans and lines of credit, it is key to make sure that the urban planners face no surprises throughout the lifetime of the development. With real-time updates on information and data as to how traffic would be changed, parking levels, capacity, or design, every subcontractor connected to the project will also have access to see this data and update its scope of work in real-time during the planning stage.
 |
|
A futuristic perspective for a museum. |
• Subcontractors/third parties: The aforementioned point also connects to third parties contributing to the development of the projects. With any development, there are insurance companies, government entities, construction, engineering, interior designing firms, and many more factors that other companies would be handling. If any change is made in the plan, it would be visible to all participants in real-time, and they would take it into consideration in a much more automated way.
• The buyers: It is also typical for projects to sell off plan or allocations years before completion of the project. While today the system relies heavily on traditional means of ‘off-plan’ sales, having a digital twin would broaden the information for more prospective buyers to come in, and drive a higher conversion rate.
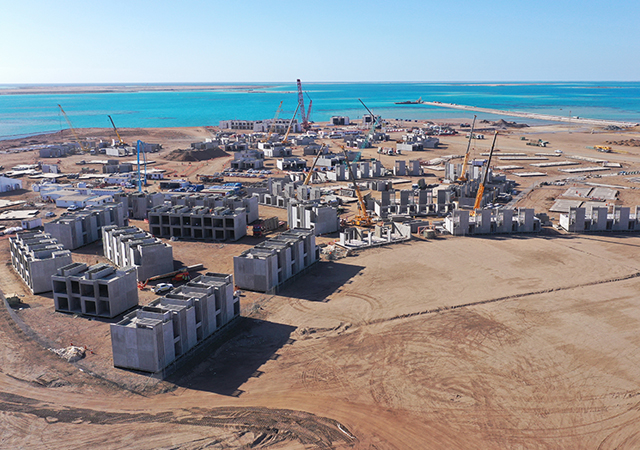
The GCC is already exemplifying the power of Digital Twin Technology (DTT): Saudi Arabia’s Red Sea Global is making eco-friendly travel spots, and Qatar’s Hamad International Airport is achieving remarkable efficiency. These are a testament to DTT’s role in modernising urban landscapes.
VIRTUAL LAND OWNERSHIP AND DEVELOPMENT
As real estate markets flourish in the Arabian Gulf, the metaverse is introducing a whole new real estate market. Individuals and companies can now own, trade, and build on virtual plots of land. This new territory is an economic frontier, as virtual land ownership becomes a new avenue for investment and growth.
Bayut, one of the largest real estate applications available in the region, has already implemented ‘floor plans’ and 3D replicas of certain houses and apartments listed on the application. However, it comes with certain limitations as they are isolated virtual environments. With the metaverse, and having a digital twin, access for the buyers would increase and, therefore, increase conversion for developers.
A notable example such as the Skylum Skyscraper in The Sandbox, created by Crypto House Capital, is proof that virtual land ownership bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds. This blend of architecture, planning, and technology offers potential financial returns.
PIONEERING THE URBAN METAVERSE
The metaverse’s influence on urban planning and architecture in the Arabian Gulf region is undeniable. With digital twins, urban planning, and virtual land in the mix, the urban landscape is on the brink of a transformation. It’s not just about changing the skyline – it’s about how we actually live and move around our cities.
* Samuel Huber is the CEO of Landvault, the largest construction company in the metaverse, having built over 100 million sq ft of virtual real estate with more than 120 full-time creators, and nearly 300 completed projects. The company expanded to Dubai earlier this year and is heavily investing in the GCC region, already building digital twins for real estate companies, amongst other projects.














.jpg)













 (1).jpg)