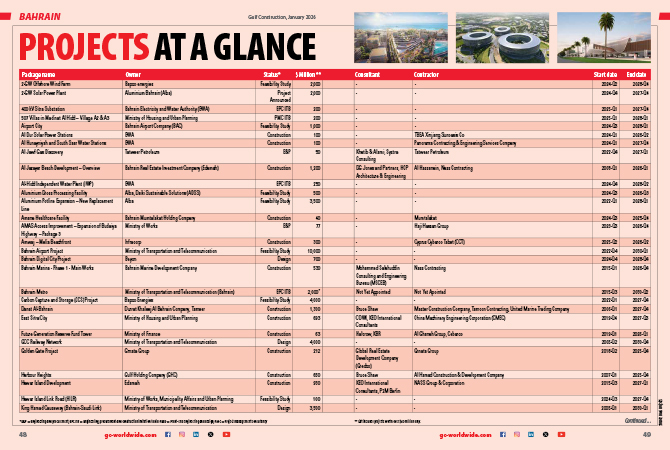
 The 3D interpolation
The 3D interpolation
International Fire Consultants (IFC) has recently announced the development of a 3D Interpolation method of assessment for the characterisation of intumescent coatings, which, according to the firm, will help in the protection of structural steelwork against fire.
The method was developed by Hans van de Weijgert, a principal engineer at IFC.
“In recent years, there have been many discussions on how best to characterise the contribution of intumescent coatings to the fire resistance of structural steelwork and it has taken many years to develop these different assessment methods,” says a spokesman for the firm.
“It is generally accepted that existing assessment methods provide a way of predicting the performance times, but with unacceptable margins of error. Due to the erroneous nature of current assessments, criteria for acceptability of results have been put into place in many standards and guidelines.”
IFC, therefore, recognised a need to develop an exact prediction of the performance times based on facts rather than estimations, he says.
“The reason that it has taken many years to study the behaviour of intumescent coatings without achieving a satisfactory characterisation method is due to the complexity of the subject, which is actually a four-dimensional problem,” the spokesman points out.
How is it done?
IFC’s assessment method takes factual data from fire tests, measures performance times and projects them into a three-dimensional space, whilst taking into account a fourth dimension, which in this case is temperature. The four dimensions are section factor (Hp/A), dry film thickness (DFT), performance time (t) and design steel temperature (T).
Advantages
Elaborating on the advantages of IFC’s 3D Interpolation method, he says: “It is based only on facts; provides the basis for assessments with negligible error; complies with criteria of acceptability by default; identifies the lower and upper limit of the DFTs for a particular value of Hp/A; and provides predictive knowledge of the performance.”
Conclusion
“The 3D Interpolation method is the only available assessment method so far that is based on facts only and will therefore render redundant all discussions of pushing, pulling or manipulating the contribution of intumescent coatings to the fire resistance performance of structural steel work.
This method has a huge potential for saving intumescent coating manufacturers large costs in research and developing by alleviating the need to carry out a large number of expensive tests.
International Fire Consultants is a division of the IFC Group of companies, which also includes IFC Certification Limited and other international subsidiaries with offices in Belgium, Holland, Cyprus and the UAE.
The principal company of the group was started in 1985, offering independent expert fire engineering and consultancy support, by Peter Jackman who is recognised internationally as an expert in fire, sitting as he does on a wide range of UK, European and International committees, as expert and UK representative.
Weijgert, a principal engineer at IFC in Princes Risborough, UK, studied the physics of the built environment and building construction in Eindhoven, The Netherlands in the 1980s. His fire testing and consultancy career started in 1987 at TNO (Nederlandse Organisatie voor Toegepast Natuurwetenschappelijk Onderzoek), the largest contract research organisation in The Netherlands, and he joined IFC in August 2000.
A specialist in the development of products, design advice for constructions on and offshore and the assessment of the fire resistance of building components and constructions, Weijgert has performed more than 2,600 full-scale fire tests in many different laboratories throughout Europe.








.jpg)



.jpg)



























.jpg)
































