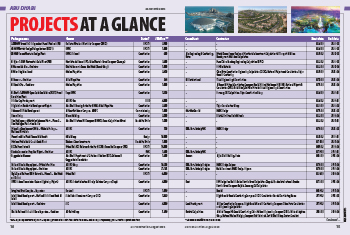
Project specifications – which are the written description of the various products (manufactured, fabricated and built) that comprise the project – serve several roles in the execution and success of a development.
They can be used as a design record, basis for costing, demonstration of regulatory compliance, basis for tendering, contract document, contract administration tool and, if worse comes to worse, in a dispute they are vital documents.
As the quality of the project specification, also has an influence on the contract cost and time, help is required in preparing them to ensure that they serve the important role that they are designed for.
Accordingly, quite a few countries have national master specifications - some more than one - along the lines of the UK’s NBS.
The concept is popular with designers such as architects and services engineers, as it simplifies the process of preparing a project specification and, if used correctly, improves the quality of the output document. The preparation, and use, of a project specification is thus less of a chore, and may even be a pleasure!
Specification sources
Project specifiers can choose from a range of sources for their project specifications - a previous project specification, an office master specification, or a national master specification.
Speed, currency, reliability and scope are the key issues in deciding which source will be used - each having a cost dimension.
The problem with using previous project specifications is that they are generally not always relevant, not comprehensive, not current, and have not had their faults corrected. Office masters that are not based on national master specifications are generally not well maintained, have limited input, and are built by ad hoc accretion, are inconsistent across offices and must be learned from scratch by new staff.
National master specifications are closer to best practice, with a consistent style and structure, and have a number of significant advantages over these two other sources. They are more current than either, are at lower cost than office masters to the same standard, free up office expertise for project work, and draw on national experience, are internally logical as there no overlaps between work sections.
Their editorial and software teams will deal with faults and errors as soon as they are aware of them. They are used by co-consultants and are familiar to estimators, builders, project managers, and others in the industry. There is no need to retrain incoming staff in their use, if they have used them in their previous office. Software is available, to speed authoring and maintenance, as is an online and telephone help service. Training is also available, including for customers overseas.
NBS
NBS – a template for project specifications, comprising comprehensive clauses, inserts and guidance - does all this, and more. For example, it can be used to manage office masters and previous project specifications, so they can be used as sources with more confidence than the DIY versions.
NBS gives the best of both worlds. NBS is structured around the Common Arrangement of Work Sections, the UK classification system. Updates are issued every four months.
The system covers fabric (in NBS Building), M&E services (in NBS Engineering Services), and NBS Landscape. Each is available in two or three levels of service. NBS Scheduler is used for projects where a schedule of works is preferred to a specification, for example, in refurbishment projects. Proprietary specification resources are embedded in all of the specification products, alongside generic material.
Internationally, besides the UK, NBS is used in 25 countries including Bahrain, the Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the UAE. As well as benefiting from this user base, NBS is a founder member of the International Construction Information Society, whose members include 17 other national master specification producers from around the world. Its mission, in part, is to improve, on an international level, communication among participants in the construction process.
NBS and UK project specifications rely on references to current British Standards and other technical documents. A couple of years ago, when NBS visited Dubai and surveyed the usage of British Standards there, it found that most fabric sections in project specifications were based on them, as were many engineering services sections. But American and local standards were also used, for example, for air-conditioning and for cement and cement-based products. An office master based on NBS could be easily developed to pick up these standards, using NBS’ clause and guidance creation facilities.
Other products
NBS, the publisher of the National Building Specification, is a part of RIBA Enterprises and owned by the Royal Institute of British Architects.
It offers a range of products and services complementing the NBS specification products. The Construction Information Service (with IHS UK), NBS Building Regulations, and RIBA Product Selector are linked to the specification products, but are also available separately. Construction Information Service (CIS) provides online access to thousands of technical documents, including British Standards, and has an edition for the Middle East.
Other NBS products include Contract Administrator, Green Construction, aecportico, Educator, the NBS Journal and NBS Training. RIBA Enterprises is responsible for the Manufacturer Network, RIBA Bookshops, RIBA Publishing, and RIBA Appointments.
Based in Newcastle upon Tyne, NBS employs more than 100 highly experienced staff in the production of the National Building Specification and its range of software subscription packages. The organisation creates innovative IT solutions and delivers high-quality products for construction industry professionals.









.jpg)




.jpg)











Doka (2).jpg)







































.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)







