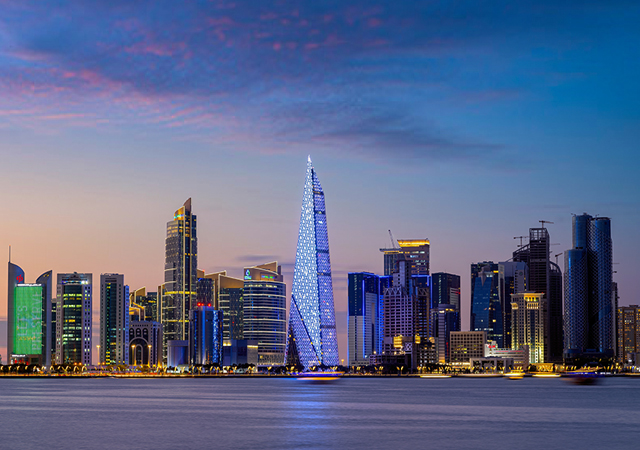
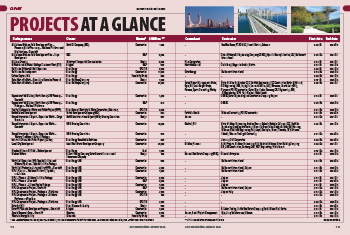
Qatar’s real estate sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as economic development, infrastructure projects and government initiatives.
Qatar’s real estate sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as economic development, infrastructure projects and government initiatives.
Qatar’s construction sector, which witnessed a significant transformation in the lead-up to the 2022 FIFA World Cup – when the nation invested heavily in infrastructure projects to cater to the mega event – is now facing a period of adjustment.
Having staged the World Cup, Qatar is left with a lasting legacy of world-class infrastructure, which the construction sector is now focused on maintaining. The stadiums, transportation systems, and accommodation facilities built for the event have not only enhanced the country’s tourism appeal but have also provided a solid foundation for future economic growth.
Qatar has grown as a global tourism destination driven by hosting such large-scale sporting events and the continuous development of tourism-related infrastructure over the past two years, according to Alpen Capital’s latest report on ‘GCC Hospitality Industry’. Its hospitality sector is projected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11 per cent (from $900 million in 2023) to $1.5 billion in 2028.
While the construction industry saw a contraction in 2023 due to the completion of major projects for the World Cup and a slowdown in new building permits, analysts in the country have noted an upswing in the sector this year which is estimated to surge by 4.4 per cent, according to a recent report by Researches and Markets.
These views were echoed by data analytics and consulting company Global Data which stated that the Qatar construction market size was $49.3 billion in 2023 and is expected to achieve an annual average growth rate (AAGR) of more than four per cent during 2025-2028. Investments in renewable energy, oil and gas, and industrial projects will result in the growth of the construction market over the period, it added.
After the lull, in fact, the total value of contracts awarded in Qatar increased by 68.5 per cent y-o-y to reach $6.1 billion during Q1 2024 as compared to $3.6 billion in Q1 2023, according to MEED Projects data. The growth in contract awards was primarily due to the jump in value of projects awarded in the oil sector during Q1 2024 which represented 80.5 per cent of the total contracts awarded in the country during the year.
The total value of oil sector projects awarded jumped from no contracts awarded in Q1 2023 to $4.9 billion during Q1 2024 with the EPC contracts to increase oil production from Al Shaheen offshore oil field.
The total value of contracts awarded in the building and infrastructure construction sector increased by 347.4 per cent to reach $519 million in Q1 of this year against $116 million in Q1 2023. Similarly, the aggregate value of contracts awarded in the power sector improved by 49.1 per cent to reach $489 million during the period.
 |
|
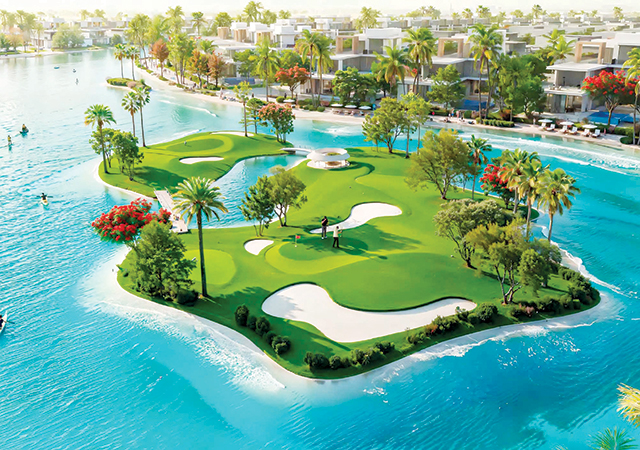
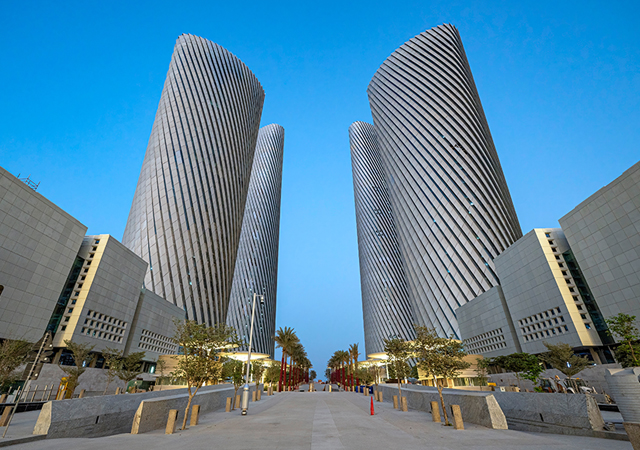
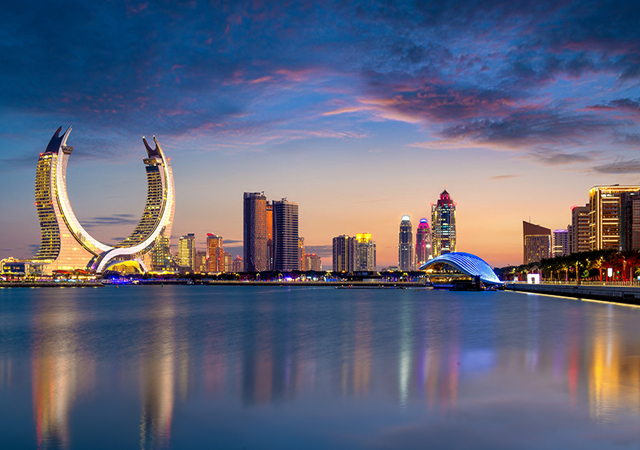
Lusail City offers significant potential for real estate investment. |
The construction and real estate sectors have contributed significantly to Qatar’s GDP in 2023 and are expected to remain important drivers of the non-oil economy. According to leading real estate platform Property Finder’s Residential Real Estate annual report, the construction and real estate sectors together grew by 3.4 per cent in 2023, contributing to almost 19 per cent of Qatar’s GDP.
The outlook for residential construction is promising with the rising foreign direct investments in the realty sector, primarily by expatriates and foreign businesspersons, with the West Bay Lagoon and The Pearl being regions of interest.
The country is now enhancing its infrastructure and industrial projects in line with the national strategy vision and to host the Asian Games 2030.
This apart, Qatar’s 2050 Transport Plan includes big-ticket projects such as an expansion of the existing Doha Metro network as well as the ambitious $12-billion Sharq Crossing, which comprises a unique bridge-tunnel connection between Katara Cultural Village and Hamad International Airport.
Growth in Qatar has essentially been public sector-led. However, the National Vision 2030 envisions an increasing more diversified, private sector-driven model. Achieving this transformation requires bold reforms to boost productivity, foster a more conducive business environment, and leverage progress in digitalisation and climate actions, according to the IMF’s latest annual economic review.
Qatar’s economic diversification efforts are anchored by the Third National Development Strategy (2024-30), launched in January, which plays a crucial role in the recovery of government revenues, reducing economic dependence on hydrocarbons and enhancing resilience to price fluctuations, the report said.
Qatar’s non-oil economy comprises two-thirds of Qatar’s gross domestic product (GDP) and has seen significant contributions from sectors such as real estate and construction, financial services, trade, manufacturing, logistics and tourism. Such sectors have not only created new revenue streams but also provided employment opportunities, supported by substantial infrastructure investments, according to IMF.
The nation has implemented a series of reforms to improve the investment climate, including easing restrictions on foreign ownership, establishing free zones, and enhancing the legal and regulatory framework for businesses – all of which have successfully attracted significant infrastructure and energy sector investments from around the world, the report added.
A number of analysts concur that the market will recover as the country persists in investing in a diverse range of infrastructure and industrial projects, aiming to meet the numerous pillars of Vision 2030.
However, key challenges for the industry remain despite a forecast for growth. Some of them include rising costs of construction, excessive lead times, and a shortage of skilled labour.
Looking ahead to 2030, industry experts noted that the current activities under way across the Middle East will see Qatar compete for labour and resources and this could potentially lead to construction cost escalation.
According to an international construction market survey by Turner & Townsend, Doha is positioned as the second-most expensive city in the Middle East to build in.
Although the mega sporting event in 2022 played a pivotal role in increasing construction prices, the industry analyst noted a downward trajectory shift for costs this year.
Roads & Metro
Qatar’s investments in its Transportation Master Plan 2050 (TMPQ) are expected to foster a range of construction projects, aiming to increase the number of visitor arrivals, said a research analyst.
 |
|
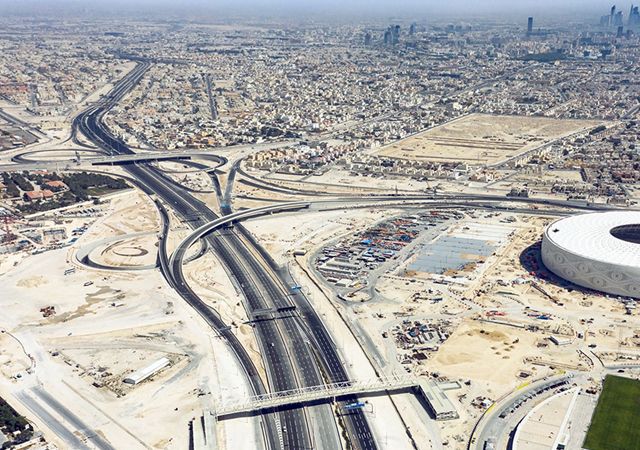
Work on upgrading the E Ring Road comprises the Mesaimeer Interchange, the first-of-its-kind project in Qatar. |
In a recent interview with The Peninsula, Colin McBride, Director of Cost Management, Qatar at Turner & Townsend, said Qatar’s transport networks are undergoing expansion as the government is investing QR9.7 billion ($2.7 billion) in its Transportation Master Plan.
Among the major projects he cited are the Doha Metro, the Bahrain-Qatar causeway, and the Sharq Crossing.
 |
|
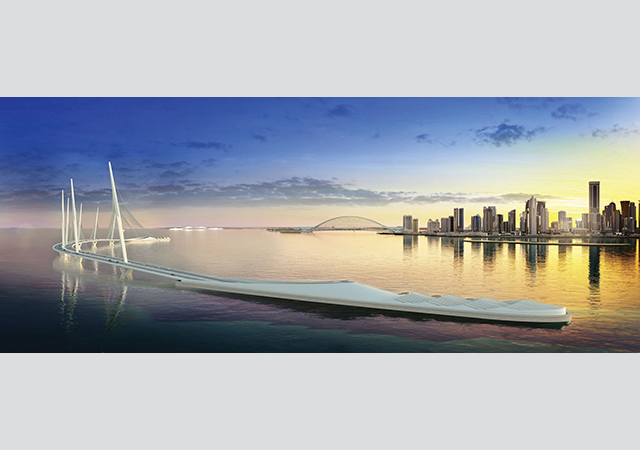
The $12-billion Sharq Crossing ... a much-anticipated project. |
The 12-km-long Sharq Crossing, which was officially launched in December 2013, counts among the largest infrastructure projects in Qatar. Designed by Spanish architect Santiago Calatrava, the bridge-tunnel connection across Doha Bay consists of three bridges, two immersed tunnels with a total length of approximately 6 km and three cut-and-cover tunnels, and a marine interchange. Work on the ambitious development was put on the backburner as it wasn’t considered a priority project for the FIFA World Cup and was expected to be restarted in the third quarter of 2020, but further updates on the project have not been released.
The Public Works Authority ‘Ashghal’, which is spearheading Qatar’s infrastructure ambitions, has been responsible for the nation’s impressive road and metro network.
Ashghal is implementing 33 projects to serve 30,000 plots of citizens through its Local Areas Infrastructure Programme across Qatar. In May, Ashghal announced that it completed infrastructure services for 7,833 plots in the north, west and south of Qatar under the programme.
Ashghal’s Local Areas Infrastructure Programme is a nationwide programme that aims to develop the roads, drainage networks and overall infrastructure in all areas of Qatar.
Among the projects completed are the Roads and Infrastructure Development projects at East Al Wajba (Package One), West Semaisma (Package One), Al Ebb and Leabaib (Package One and Package Five), West Muaither (Package 2), and the main works in Al Egda, Al Heedan and Al Khor (Package One), located west of Al Bayt Stadium.
Another major development is the construction and upgrading of E Ring Road, which comprises the Mesaimeer Interchange, the first-of-its-kind project in Qatar connecting six main roads and providing a vital traffic link between the south, central and north of the country.
Oil, Gas & Industry
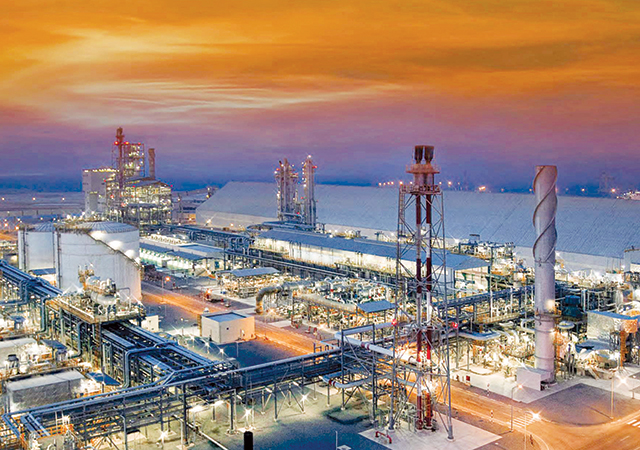
Qatar is reliant on its hydrocarbon exports, which have propelled the nation to become one of the world’s wealthiest economies. Hence, it is but natural that the country is making massive investments in boosting its oil and gas upstream and downstream sectors.
Last month, QatarEnergy LNG awarded Saipem a $4-billion offshore EPC contract aimed at sustaining the production of the North Field offshore natural gas reservoir, located off the north-east coast of Qatar.
This followed the four main engineering, procurement, construction, and installation (EPCI) contract packages worth a total of more than $6 billion awarded by QatarEnergy for the next development phase of the offshore Al-Shaheen field (Qatar’s largest oil field) to increase production by about 100,000 barrels of oil per day (bpd).
These EPC packages were for:
• Nine wellhead platforms valued at about $2.1 billion and awarded to a consortium of McDermott Middle East and Qingdao McDermott Wuchuan Offshore Engineering;
• A central processing platform valued at about $1.9 billion assigned to a consortium of McDermott Middle East and Hyundai Heavy Industries;
• A riser platform worth about $1.3 billion and awarded to Larsen & Toubro;
• Subsea pipelines and cables valued at about $900 million to be carried out by China Offshore Oil Engineering Co (COOEC).
Late last year, HH the Amir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al-Thani laid the foundation stone of the North Field expansion, which will raise Qatar’s LNG production capacity from the current 77 million tonnes per year (mtpy) to 126 mtpy by 2026.
Claimed to be the world’s largest LNG project, the project includes six mega trains, each with a production capacity of 8 mtpy of LNG. In addition, it will produce 6,500 tons per day of ethane gas, which will be used as a feedstock in the local petrochemical industries.
In line with these developments, in February this year the Amir laid foundation stone for the $6-billion Ras Laffan Petrochemical Complex at the Ras Laffan Industrial City. The complex will house an ethane cracker with a capacity of 2.1 million tons per annum of ethylene.
This massive investment will also increase Qatar’s overall petrochemical production capacity to nearly 14 million tons per annum. The project is among the largest globally includes two polyethylene trains with a combined annual output of 1.7 million tons of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) polymer products.
In addition, QatarEnergy last month announced its decision to build a world-scale urea production complex that will more than double the country’s urea production. The new mega project entails building three ammonia production lines that will supply feedstock to four new world-scale urea production trains in Mesaieed Industrial City.
Real Estate
Qatar’s real estate sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as economic development, infrastructure projects, and government initiatives. The country’s focus on sectors like logistics, tourism, and manufacturing, as outlined in the Third National Development Strategy (NDS3), has also boosted demand for real estate.
The real estate sector is expected to continue growing steadily, reaching a value of $41.6 billion by 2028.
Qatar’s robust economy and high GDP per capita provide a solid foundation for real estate growth while the government’s recent initiatives to promote real estate development, including the establishment of RERA to regulate the sector and Real Estate Platform of Qatar (QREP) – a centralised online portal offering accurate data and statistics about real estate sector – are playing a crucial role in enhancing transparency and attracting investment.
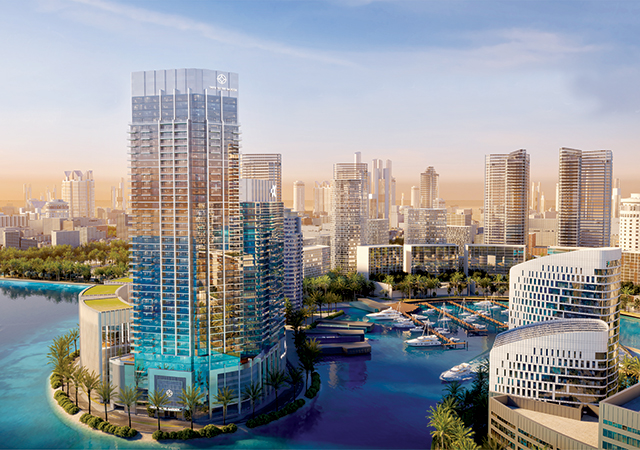
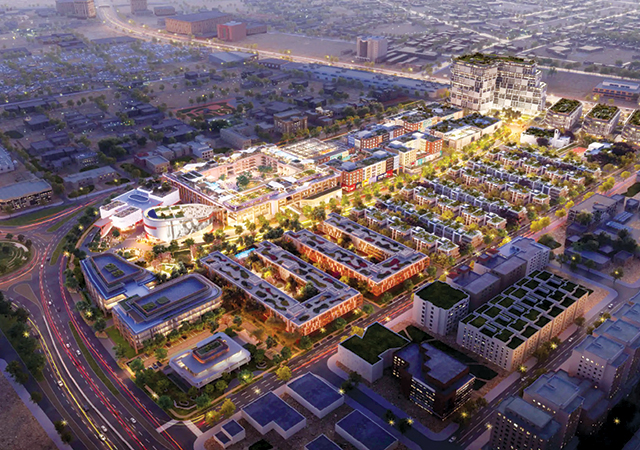
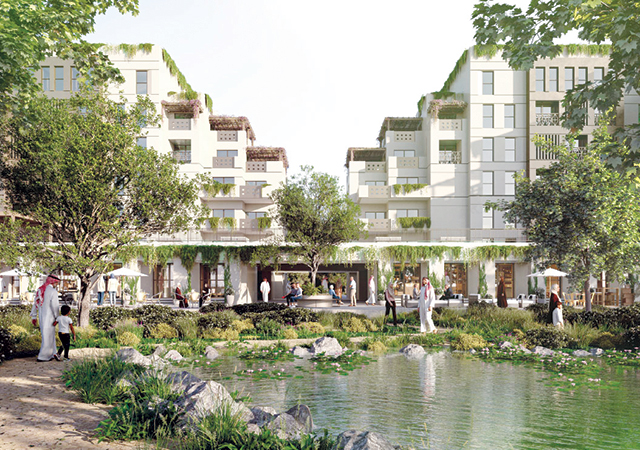
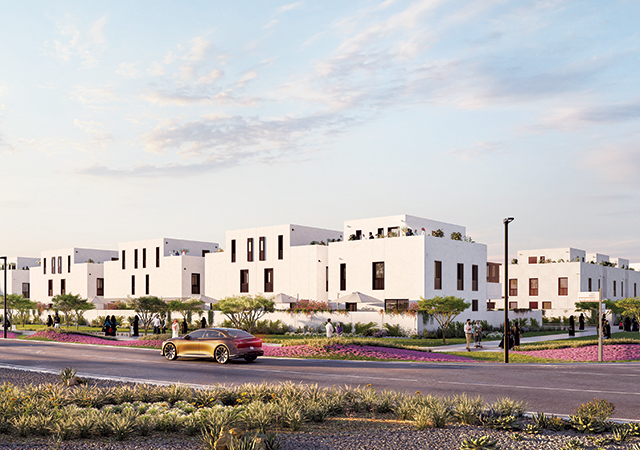
Ongoing infrastructure projects, such as the expansion of Lusail City, are creating opportunities for real estate development. As a major economic hub and entertainment destination, Lusail City offers significant potential for real estate investment.
One such massive development that is nearing completion is the 1.1 million-sq-m Foster + Partners-designed Lusail Plaza Towers, which comprises four distinctive high-rise buildings, two of which are the tallest in Qatar standing at 301 m tall (see Page 14).
The residential and mixed-use real estate sectors accounted for a substantial portion of ongoing projects in 2023, with private sector development dominating the market. The private sector contributed 92.6 per cent of the total number of ongoing projects till the end of 2023 and almost 84.5 per cent of the total investments worth $11 billion in ongoing projects until the end of 2023.
According to Property Finder, the residential and mixed-use real estate sectors recorded a total of 157 ongoing projects worth $19.1 billion last year. These projects accounted for 61.8 per cent of the total investments.
Qatar has seen growing demand for residential properties in recent months and industry sources state that more than 6,000 units – most of them apartment buildings – are in the pipeline for the current year.
According to several analysts in the country, the residential construction market size is anticipated to amount to $12.39 billion in 2024 and will reach $21.32 billion by 2029. Experts at Researchers and Markets noted that the sector is growing at a CAGR of 11.45 per cent in the next five years.
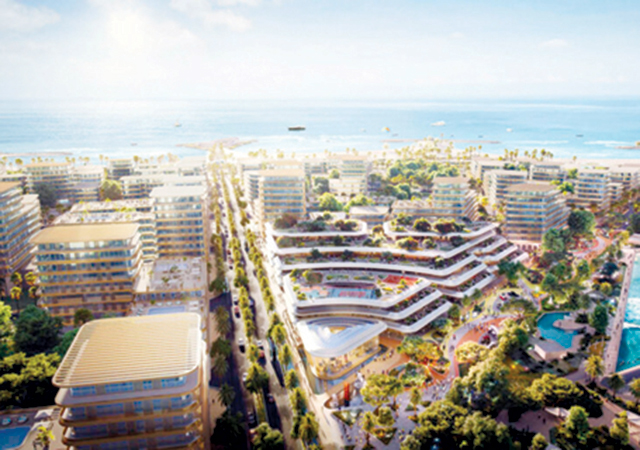
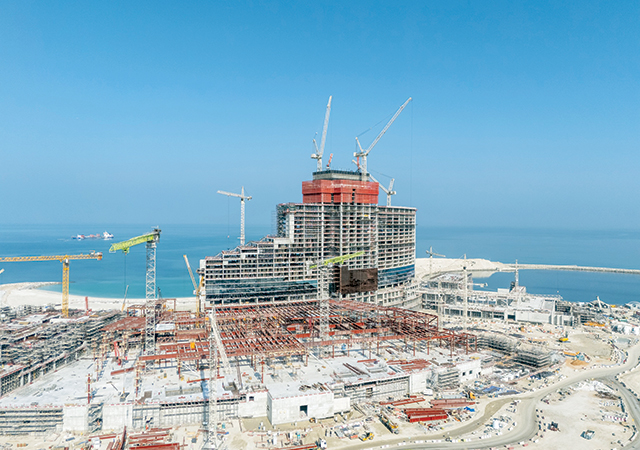
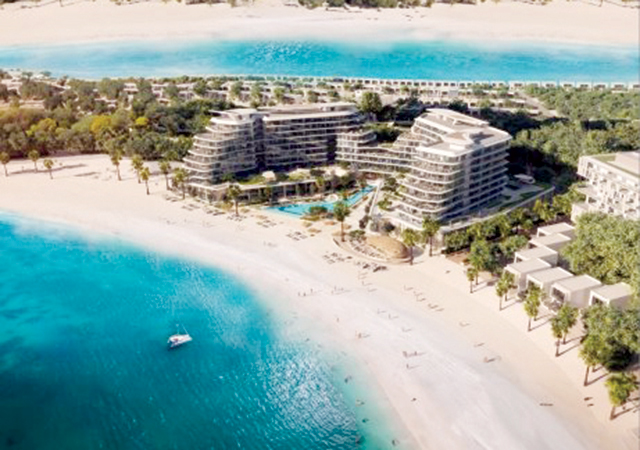
Among the most impressive projects launched this year is the $5.5-billion Smaisma Project, which is expected to become Qatar’s new urban landmark. Managed by Qatari Diar Real Estate Investment Company, the project has been planned under the umbrella of the Ministry of Municipality (see Page 16).
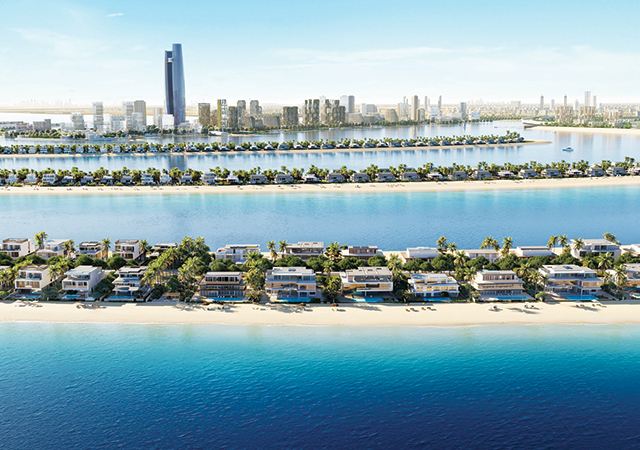
Another major development is the Qetaifan Island North project, which is owned by Qetaifan Projects and being developed by JMJ Group Holding.
Zaha Hadid Architects (ZHA), the award-winning architectural and design practice, was signed up late last year to design multi-use buildings on seven medium-rise land plots along the southern waterfront of Qetaifan Island North. The QR986-million project is estimated to cover nearly 40,000 sq m. According to Zaha Hadid Architects, the development’s design would cultivate a strong sense of community, connect residential and urban environments, and represent the future of luxury living.
Power & Water
In line with Qatar’s Sustainability Strategy, QatarEnergy last month announced that it will build a new mega solar power project that will more than double the country’s solar energy production, significantly contributing to lower carbon emissions in the framework of a realistic energy transition.
The new project will double Qatar’s PV solar power production capacity to about 4,000 MW by 2030 by building one of the world’s largest solar power plants in the Dukhan area, with a production capacity of 2,000 MW.
Educational facilities
Qatar is also joining hands with the private sector to build schools. Among the initiatives this year, Ashghal has tied up with Urbacon Trading and Contracting Company to build 14 schools under a public-private partnership (PPP) agreement. The schools, which will accommodate more than 10,000 students, are scheduled to be operational from the 2025-26 academic year.
This is part of the second package of the Qatar Schools Development Programme within the PPP projects, in cooperation with the Ministry of Commerce and Industry and the Ministry of Education and Higher Education.
Ashghal had overseen the construction of the first package of eight schools through the PPP initiative.
Meanwhile, construction work is currently under way on the colleges of Medicine and Health Sciences at Qatar University, which will cater for around 1,470 students. The new four-storey buildings will cover a total area of about 36,000 sq m. The project is expected to be delivered in early 2026.













.jpg)